Introduction to Electric and Hydrogen Cars

The automotive world is buzzing with innovation, and two technologies are leading the charge: electric cars and hydrogen cars. As we shift toward sustainable transportation, these vehicles promise to reshape our roads and reduce our carbon footprint. But which option truly holds the key to a greener future? Electric cars have gained popularity for their convenience, while hydrogen cars boast impressive efficiency. Join us on this journey as we explore how these groundbreaking technologies work, their advantages and disadvantages, environmental impacts, costs, infrastructure challenges, and ultimately determine what might be next in the race towards sustainability.
How Do They Work?
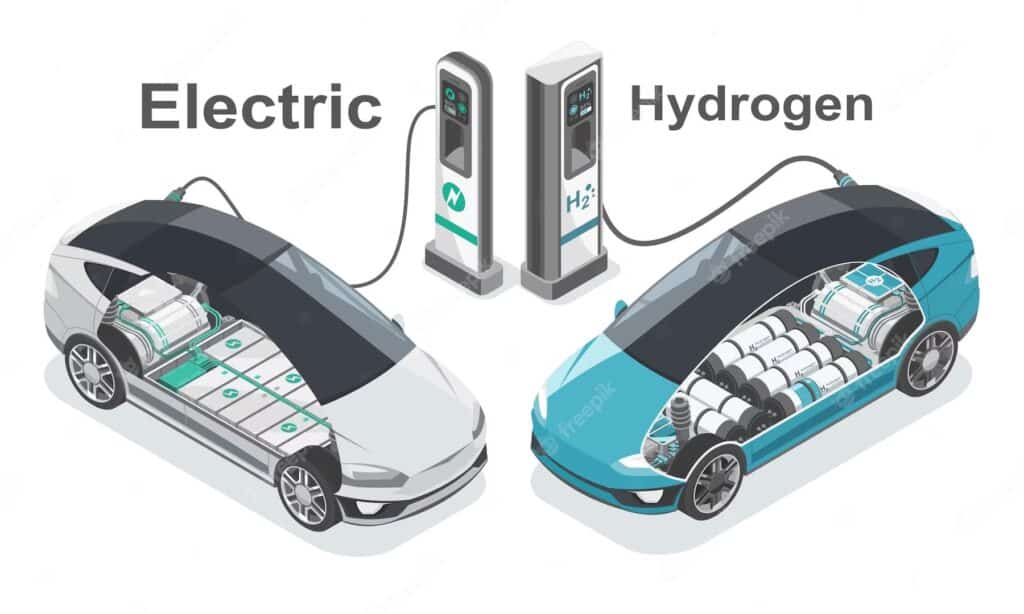
Electric cars operate using a simple but effective mechanism. They harness electricity stored in batteries to power an electric motor. When you press the accelerator, energy flows from the battery to the motor, propelling the car forward.
Hydrogen cars take a different route. They utilize hydrogen gas stored in tanks, which feeds into a fuel cell. This process combines hydrogen with oxygen from the air to create electricity and water vapor as byproducts. The generated electricity then powers an electric motor similar to that of traditional electric vehicles.
Both technologies promise zero tailpipe emissions, contributing positively toward cleaner urban environments. However, their methods highlight distinct pathways for achieving sustainable transportation solutions in our evolving automotive landscape.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Electric Cars
Electric cars have gained immense popularity due to their eco-friendly nature. They produce zero tailpipe emissions, which significantly reduces air pollution. This benefit aligns well with global efforts to combat climate change.
However, the initial cost of electric vehicles can be a barrier for many consumers. While prices are dropping, they still tend to be higher than traditional combustion engines.
Charging infrastructure is another concern. Though it’s improving rapidly, charging stations may not always be conveniently located in rural areas or during long trips.
Battery life and range anxiety also pose challenges for potential buyers. Although technology is advancing quickly, some drivers worry about running out of charge on longer journeys.
Despite these drawbacks, electric cars offer quiet operation and lower maintenance costs over time. They’re an attractive option for those looking to reduce fuel expenses and environmental impact.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Hydrogen Cars
Hydrogen cars present a fascinating alternative to traditional electric vehicles. One major advantage is their quick refueling time, akin to filling up a gasoline tank. This convenience can easily fit into busy schedules.
Moreover, hydrogen fuel cells produce only water as exhaust, making them eco-friendly in operation. They offer longer driving ranges compared to many battery-electric models, appealing for long-distance travel.
However, challenges exist. The production of hydrogen often relies on fossil fuels, raising concerns about its overall environmental impact. Additionally, the infrastructure for hydrogen refueling stations remains limited in most regions.
Cost is another hurdle; hydrogen vehicles tend to be more expensive upfront compared to electric cars. Maintenance costs are also uncertain due to fewer experienced mechanics familiar with this technology at present.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of electric cars and hydrogen cars is a hot topic. Both technologies aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, but they do so in different ways.
Electric vehicles (EVs) run on batteries charged from the grid. If that electricity comes from renewable sources like wind or solar, their carbon footprint shrinks significantly. However, battery production can be resource-intensive and environmentally taxing.
Hydrogen cars convert hydrogen fuel into energy through a chemical reaction with oxygen. While this process emits only water vapor, producing hydrogen often involves fossil fuels unless generated sustainably.
Another concern involves infrastructure for both types of vehicles. EV charging stations are spreading rapidly; however, hydrogen refueling stations remain limited in number and availability. This gap could affect adoption rates for each vehicle type moving forward.
As we consider our choices today, it’s crucial to weigh these factors against long-term sustainability goals and advancements in technology.
Cost Comparison
When comparing electric and hydrogen cars, cost is a crucial factor. Electric vehicles (EVs) typically have lower upfront costs than their hydrogen counterparts. This is largely due to the more complex technology involved in producing hydrogen fuel cells.
Charging an EV at home can be quite economical, especially with various energy plans available. On the other hand, fueling a hydrogen car often requires specialized stations that may not be as widespread or accessible yet.
Maintenance costs also differ significantly. Electric cars generally require less maintenance because they have fewer moving parts compared to hydrogen vehicles which involve intricate fuel cell systems.
However, government incentives for both types may influence initial expenses and long-term savings. Each option offers unique financial advantages that depend on individual needs and local infrastructure developments.
Availability and Infrastructure
The availability of charging stations and fueling stations is crucial for the adoption of electric and hydrogen cars. Electric vehicles (EVs) benefit from a rapidly expanding network of charging infrastructure. Many cities now offer public chargers, making it easier to recharge during errands or commutes.
On the other hand, hydrogen fueling stations are still relatively scarce. This limits the practicality of hydrogen cars in many regions. While some areas have embraced this technology, others lag behind significantly.
Moreover, governments are investing in both infrastructures with varying degrees of success. EV charging networks are growing faster due to consumer demand and technological advancements.
For those considering a switch to alternative fuels, understanding local availability can make all the difference in daily usability and convenience when choosing between electric or hydrogen options. Each option presents unique challenges that impact user experience directly related to available infrastructure.
Which is Better for the Future?
When considering the future of transportation, both electric and hydrogen cars present compelling cases. Electric vehicles have gained significant traction due to their established technology and growing infrastructure. Their popularity is bolstered by advancements in battery efficiency and charging networks.
On the other hand, hydrogen cars offer a promising alternative with faster refueling times and longer ranges. They can also utilize existing fuel infrastructures, which could ease adoption challenges.
However, one must consider energy sources used for hydrogen production. If derived from renewable resources, it holds immense potential; otherwise, its environmental benefits may diminish.
Consumer preferences are shifting as people become more environmentally conscious. Automakers are investing heavily in both technologies to meet diverse demands globally.
The path forward may not be about choosing one over the other but rather finding a balance that incorporates both innovations into our daily lives.
Conclusion
The landscape of the automotive industry is evolving rapidly as consumers and manufacturers alike seek sustainable solutions. Electric cars have surged in popularity due to their efficiency, ease of use, and expanding infrastructure. Meanwhile, hydrogen cars present an intriguing alternative with their rapid refueling times and longer ranges.
Each technology offers distinct advantages that cater to different needs. The environmental implications are significant for both options, showcasing a commitment to reducing fossil fuel dependency. Cost remains a critical factor; while electric vehicles may be more accessible now, hydrogen’s potential could reshape future markets if infrastructure investments continue.
The direction we take depends on advances in technology, consumer preferences, and government policies supporting clean energy initiatives. Both electric and hydrogen cars will likely coexist in various forms as we navigate towards greener transportation solutions. The journey ahead promises innovation and excitement for what’s next on our roads!










